Across every major industry, companies are adopting automated decision systems at a pace we have never seen before. These systems now guide claims routing, forecasting, fraud checks, support workflows, supply chain planning, and customer decisions.
As adoption grows, so does the impact of every action these systems take. That is why AI governance has become one of the most important priorities for leadership teams in 2026.
AI governance is no longer a topic reserved for researchers or policy groups. It is now a fundamental part of how companies manage risk, maintain trust, and protect their operations. When these systems work, they improve productivity and service quality. When they fail, they create exposure that spreads across finance, compliance, operations, technology, and customer relationships.
A recent Gartner study reports that 55 percent of large companies will rely on automated decision systems in mission-critical workflows by 2026.
At the same time, IBM’s Global AI Adoption Index found that 79 percent of executives are concerned about the risks of ungoverned AI, yet only a small portion have a formal governance structure in place.
This gap between growth and oversight is what creates risk. AI governance closes that gap. It provides a clear set of rules, responsibilities, and guardrails that guide how systems are designed, deployed, and monitored. It also helps you prepare for new regulations arriving across the US, UK, EU, and Asia.
In this guide, we break down what AI governance means, why it matters, how it works across the enterprise, and what steps your teams can take to build a governance program that is both practical and effective.
What is AI Governance
AI governance is the structure that ensures your automated systems behave in ways that are safe, fair, and aligned with your goals. It combines policies, controls, oversight, testing, and monitoring to keep systems reliable as they evolve.
A simple way to understand governance is to view it through three questions:
- Are we using systems that match our business rules and legal responsibilities?
This covers data use, decision logic, transparency, and compliance.
- Do we understand how these systems influence outcomes?
This requires clear documentation, explainability, and predictable behavior.
- Can we control and correct the system when something changes?
Governance ensures you can audit, monitor, adjust, and intervene when needed.
Strong governance does not slow innovation. It helps you scale without losing visibility or control. It provides the stability leadership teams want while supporting growth in automation.
Read More: Multi-Tenancy in Cloud Architecture
Why AI Governance Is Essential in 2026
AI governance matters now more than ever because adoption is rising quickly while regulations tighten around the world.
Regulation is evolving fast
The EU AI Act sets the world’s first broad regulatory structure for automated systems. Companies that use “high-risk systems” must prove safety, explainability, human oversight, and data quality.
In the US, the White House Executive Order on Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy AI calls for new standards around testing, reporting, and oversight.
In the UK, regulators have adopted a “pro-innovation” model that still requires fairness, transparency, and risk management. You can check: UK Government AI Regulation Framework
These rules place responsibility on companies to prove that their systems are well-managed.
Operational risk is rising
McKinsey reports that 41 percent of companies experienced unexpected model failures in the past year, often due to changes in data, workflows, or conditions.
These failures can lead to incorrect approvals, wrong risk scores, poor predictions, or service outages. AI Governance helps teams catch issues early and fix them before they spread.
Bias and fairness concerns continue to grow
In the 2025 landscape report, the AI Now Institute highlights that automated systems can reinforce unfair patterns when data is incomplete, unbalanced, or poorly monitored. Governance helps you identify and correct these issues before they affect customers or employees.
Cost and cloud usage must be controlled
Cloud bills can climb quickly when automated systems scale. Flexera’s 2024 Cloud Survey found that 82 percent of companies saw unexpected cloud cost spikes tied to ML workloads. Governance includes usage controls, monitoring, and budgeting to keep costs predictable.
Read More: Why CFOs Should Partner with Gen AI-Powered MSPs
The Pillars of a Strong AI Governance Program
AI governance is easier to understand when broken into clear pillars. These pillars help you create consistency across the organization.
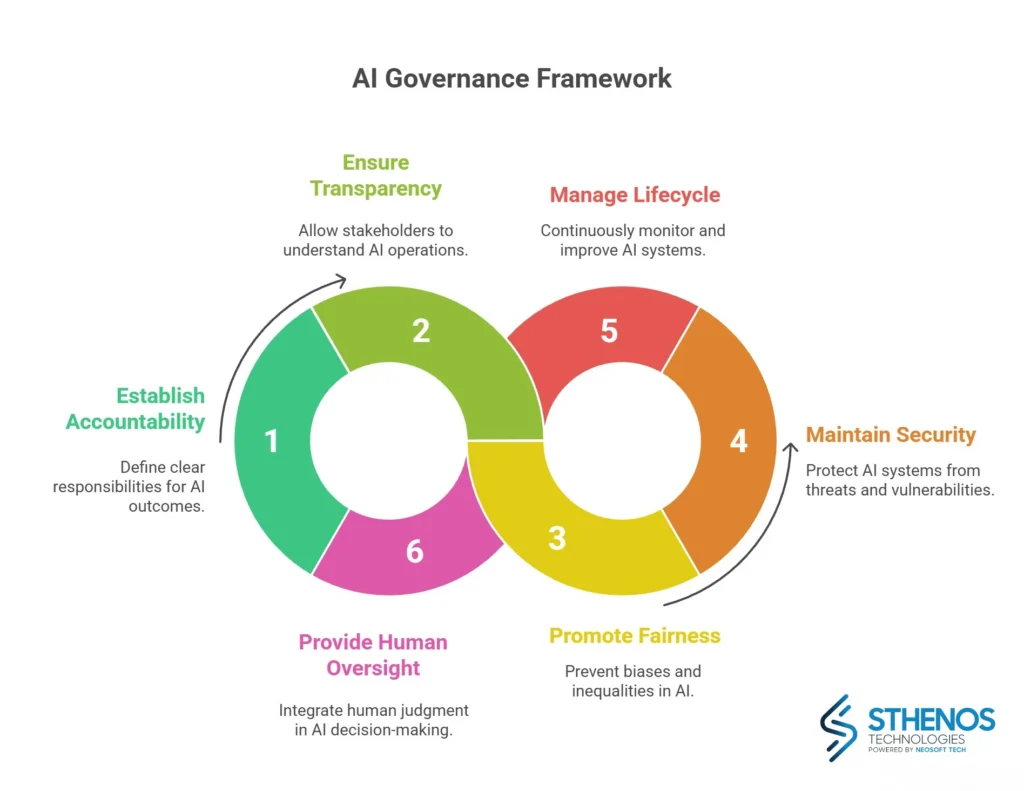
1. Accountability and ownership
Clear ownership reduces confusion and speeds up issue resolution. Someone must own:
- the system
- the data
- the decisions
- the performance
- the review cycle
Without ownership, risks spread across teams.
2. Transparency and explainability
Your systems need to provide clear reasons for their outputs.
This does not require deep technical knowledge. It requires:
- documented logic
- plain-language summaries
- access to decision history
Explainability builds trust across leadership teams and supports compliance reviews.
3. Fairness and safety
Companies must test systems to ensure decisions do not favor or harm specific groups. Governance includes fairness checks, scenario testing, and ongoing monitoring across customer journeys.
4. Security and data protection
AI systems depend on high-quality, well-secured data. IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report shows that the average breach costs $4.45 million, and systems with weak data controls face higher risks. Data governance ensures your pipelines remain compliant and secure.
5. Lifecycle management
Every system must be tracked from design through deployment and beyond. Lifecycle governance includes:
- version control
- performance checks
- drift monitoring
- documentation
- approval processes
This prevents surprises and keeps your systems aligned with current business needs.
6. Human oversight
Humans remain in control. AI governance requires review steps, approval gates, and escalation paths when outcomes fall outside expected behavior.
Why Agent Systems Require Even Stronger Governance
Agent systems behave differently from traditional models. They complete tasks across several steps, call tools, update information, and interact with systems over long periods. This creates unique governance needs.
With agents, governance must cover:
- tool permissions
- action boundaries
- task logs
- long-running workflows
- data access control
- memory rules
- safe handoffs
Because agents can chain actions together, even small errors can spread. Governance prevents this by defining clear limits and review paths.
Leaders do not need to understand the technical details. They need to know that risks are controlled, monitored, and documented.
Key Risks AI Governance Must Address
Compliance exposure
The EU AI Act includes fines of up to 7 percent of the global revenue for high-risk violations. Companies must show clear documentation and testing to remain compliant.
Operational instability
Deloitte research highlights that data drift alone can lower model accuracy by 20 to 40 percent if not monitored. Governance sets rules to detect and correct drift.
Ethical concerns
Systems can behave unfairly without proper data checks. This affects hiring, lending, pricing, and customer decisions. Strong governance catches these issues early.
Financial impact
Automation without governance can create errors at scale. It also increases cloud costs when workloads grow unchecked. Governance helps you manage efficiency and spend.
Read More: Why Legacy System Modernization Needs a Gen-AI Approach
How to Build an AI Governance Program: A Practical Blueprint
A strong governance program grows in stages. You do not need to do everything at once. You need structure and steady progress.
1. Start with a governance charter
Define goals, scope, roles, and review cadence. Set clear expectations for leadership, technology, and compliance teams.
2. Build an AI system inventory
List all automated systems across your organization. Include:
- data sources
- workflows
- owners
- purpose
- risk level
This inventory becomes your map.
3. Classify systems by risk
Not all systems need the same oversight. Create simple categories:
- low risk
- moderate risk
- high risk
Assign governance depth based on risk, not complexity.
4. Design clear data and access controls
Good data is the foundation of safe systems. You need:
- data quality rules
- access permissions
- usage logs
- retention policies
Controls reduce errors and protect privacy.
5. Build pre-deployment testing standards
Before a system launches, test for:
- fairness
- accuracy
- safety
- resilience
- regulatory compliance
Testing helps you avoid downstream failures.
6. Set up continuous monitoring
Use dashboards and alerts to watch for:
- drift
- performance drops
- unusual patterns
- data changes
Monitoring keeps systems stable in real conditions.
7. Train teams
Governance is not a technology activity. It involves your whole organization. Teams need training on roles, expectations, review steps, and incident handling.
Industry-Specific Governance Requirements
Different industries face different risks. Your governance plan should reflect this.
Finance: Systems help manage loans, fraud checks, credit scoring, and forecasting.
Regulators require clarity, fairness, documentation, and strong controls.
Healthcare: Systems support patient intake, scheduling, and record management.
Governance protects patient safety and privacy under HIPAA and similar laws.
Retail and e-commerce: Systems influence pricing, recommendations, and customer experience. Governance ensures transparency and avoids unfair treatment.
Manufacturing: Systems help with planning, quality control, and maintenance. Governance keeps production safe and stable.
Public sector: Government systems impact citizens directly. Governance ensures fairness, access, and public accountability.
AI Governance Tools and Frameworks
Governance is supported by tools that help you track, audit, and monitor your systems. These include:
- data lineage tools
- drift detection tools
- fairness and testing frameworks
- monitoring dashboards
- workflow audit systems
- access control tools
These tools do not replace governance. They make it possible to run governance at scale.
Final Thoughts
AI governance gives your company the structure it needs to scale automated systems safely. It protects your operations, your customers, and your reputation. It helps you move faster without losing control. It creates trust across your organization and prepares you for new regulations and new technology shifts.
The strongest governance programs are built over time, not overnight. You start simple. You grow as your systems grow. You improve every quarter. Over time, governance becomes part of how your organization works, not an add-on.
If you build governance now, you will be ready for the next decade of automation, complexity, and opportunity.
At Sthenos, we help you with AI services to map your systems, classify risk, build oversight pathways, monitor systems at scale, design safe agent workflows, strengthen compliance, create dashboards for leadership and support teams with training.
If you want a practical governance plan that fits your business, we are here to help. Schedule a consultation with one of our AI experts.