There are two main types of AI agents in use today: one is horizontal, and the other is vertical. Each serves a different purpose and offers unique strengths and limitations. To make the right technology choices, you need to understand how these two compare and how they fit into your business.
At Sthenos, we help teams build and scale both types of agents. What we see every day is simple. You get the best results when you know exactly what each type can and cannot do.
In this blog post, we’ll explain the difference between horizontal and vertical AI agents along with their advantages and limitations. We’ll also explain the use case across industries and which one you should consider for your business.
What is a Horizontal AI Agent?
A horizontal agent is built to handle a wide range of general tasks. It is flexible and can switch across multiple topics. You can use it for research, writing, planning, summaries, basic support, and many other jobs that do not require deep subject knowledge.
Horizontal agents are popular because they are quick to deploy and easy for your teams to test. You don’t need domain training or a lengthy setup time. This makes them a good starting point for companies exploring automation.
The downside is accuracy. Since a horizontal agent works across many topics, it may miss context or skip important details. Research from MIT reported accuracy dips of up to 30% when systems are used outside their trained domain.
This means horizontal agents work best for tasks where errors are low risk and flexibility matters more than precision.
Read More: Multi-Agent Systems in AI
Advantages of Horizontal Agents
Easy to Deploy Across the Company: You can roll out a horizontal agent without long training cycles. Teams understand how to use it because the tasks are familiar. This enables quick adoption with minimal friction.
Supports Multiple Workflows: Marketing, HR, operations, sales, and finance teams can all use the same general agent. This makes your automation setup stable and easier to manage.
Lower Cost to Start: You do not need industry-specific data or workflow design to get value. This lets you move faster and reduce early investment.
Good for Creative or Open-Ended Work: These agents can brainstorm, structure ideas, rewrite content, answer general questions, and support early project stages. They help teams work faster without needing domain logic.
Limitations of Horizontal Agents
Lower Accuracy in Complex Workflows: A horizontal agent may struggle when the task has strict rules or when the outcome must be exact. This is where domain agents perform better.
Higher Supervision Needs: Since it works with general knowledge, you need more human review for tasks that affect customers, compliance, or financial data.
Limited Ability to Handle Regulated Work: Industries like healthcare, banking, or insurance need clear rules and structured steps. Horizontal agents do not perform well without domain training.
Not Ideal for Repetitive, Rule-Based Processes: If the workflow has the same steps every time, a vertical agent will be faster, safer, and more accurate.
Read More: Agentic AI vs Generative AI vs Traditional AI
What is a Vertical AI Agent?
A vertical agent is designed for a specific industry or workflow. It understands the rules, data, terms, and steps of that field. You can use it for finance operations, claims processing, compliance checks, retail inventory work, patient intake, or quality control.
Since it is focused on a single domain, a vertical agent is more accurate and more predictable. A study by Accenture noted that industry-trained systems reached 40 percent higher task accuracy in regulated workflows such as finance or healthcare.
This makes vertical agents suitable for tasks where mistakes are costly, compliance matters, or repeatable steps must be followed.
The tradeoff is flexibility. A vertical agent cannot jump across topics like a horizontal agent. It also needs clean domain data before you deploy it.
Advantages of Vertical Agents
Higher Accuracy and Reliability: Because a vertical agent follows domain rules and trained workflows, it produces more consistent and reliable results. This is key for CFOs, compliance teams, and operations managers.
Fits Into Your Existing Process: Vertical agents follow the same steps your workers follow today. They slot into billing, claims, reconciliation, identity verification, or supply chain tasks without major changes.
Supports Regulated and High-Stakes Work: These agents understand the data formats, approval paths, policy rules, and error handling required for regulated sectors. This reduces risk and improves compliance.
Reduces Errors in Repetitive Work: Deloitte reported that domain-based automation cut process errors by 29% in the first year. This gives you tangible quality gains and lower rework costs.
Limitations of Vertical Agents
Needs Clean Domain Data: A vertical agent depends on accurate records, structured fields, and well-defined processes. If your data is messy, you need a cleanup step before full deployment.
Longer Setup Time: You need to define rules, workflows, and exception cases. This takes more time than a horizontal rollout, but the payoff comes in accuracy.
Lower Flexibility Across Teams: You cannot deploy one vertical agent across every department. Each domain needs its own specialist agent.
Scaling Needs Planning: If you want to expand to more workflows, you need to model each one. This adds effort but ensures quality and consistency.
Read More: AI Governance: The 2026 Enterprise Blueprint
Horizontal AI vs Vertical AI Agent: Differences in Business Use
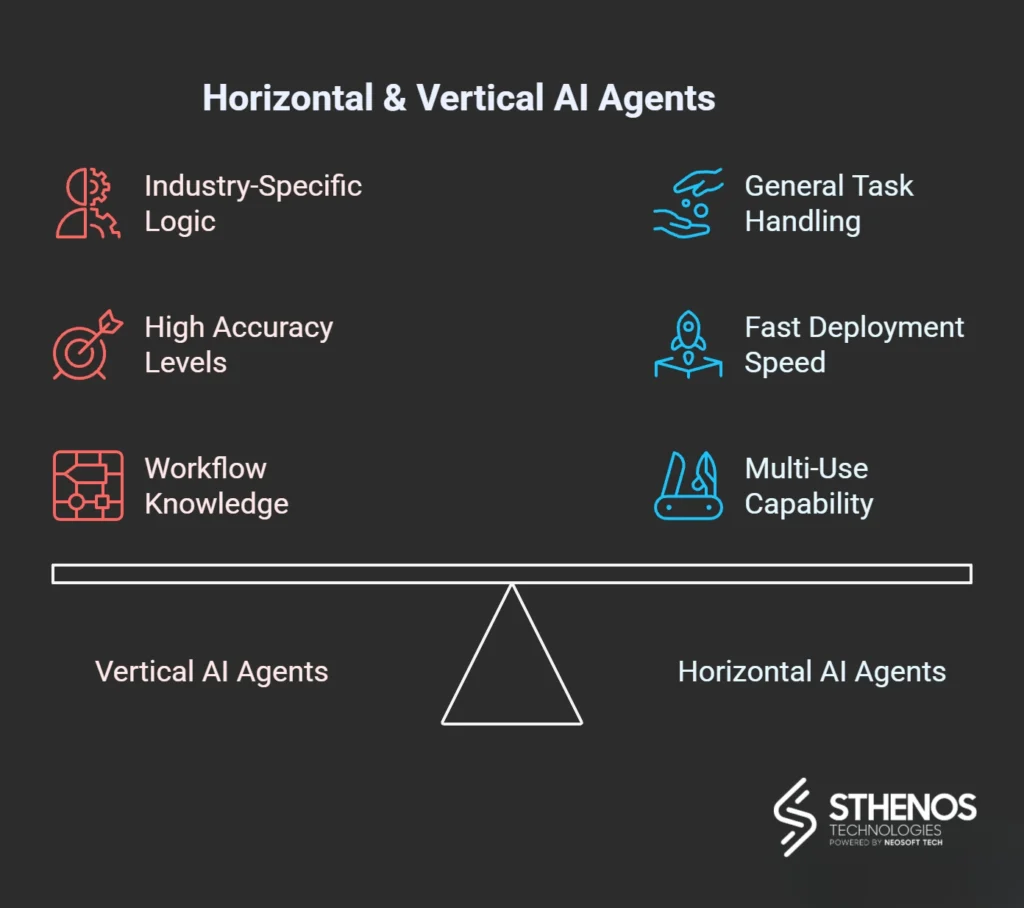
When you compare the two, the differences become clear.
Breadth vs depth
Horizontal agents give you reach. They support many teams and many tasks. Vertical agents give you depth. They deliver high accuracy in one department or one workflow.
Speed vs precision
Horizontal agents get you running fast. Vertical agents take a little longer to set up but deliver more reliable results.
Lower risk vs higher risk workflows
General support roles fit the horizontal model. Billing, forecasting, risk checks, and claims management fit the vertical model.
General knowledge vs domain logic
Horizontal systems use broad knowledge. Vertical systems rely on domain rules, internal datasets, and structured workflow paths.
Both types have a place in your business. The right choice depends on what you are trying to improve.
When You Should Use a Horizontal AI Agent
A horizontal AI agent is useful when you need a general helper. You can use it across departments and teams. Many companies deploy them to cut down the time workers spend on tasks such as research, note-taking, email responses, summaries, planning, and content drafting.
These tasks share three traits. They change often. They do not require strict rules. They do not have a high risk. This is where flexibility matters.
Gartner reported that more than 70% of companies now utilize general automation tools for everyday tasks because of the time savings they offer.
If your goal is quick wins across the company, a horizontal agent is the right fit.
When You Should Use a Vertical AI Agent
A vertical AI agent is the better choice when the workflow has clear rules, high stakes, and strong compliance needs. These tasks include:
- finance reporting
- invoice approvals
- claims management
- quality inspection
- fraud checks
- customer identity verification
- supply chain planning
These are areas where accuracy is critical. Errors can hurt your customers, your controls, or your revenue.
Deloitte found that companies using domain-focused automation saw 33 percent faster cycle times and 29 percent fewer process errors in the first year. This is why many CFOs and COOs view vertical agents as a core part of their digital transformation strategy.
Real Examples of How Horizontal & Vertical AI Agents Are Used
It is easier to see the difference between vertical and horizontal agents when you look at real industries. In most cases, you do not choose one or the other. You use both, but for different parts of the work.
Retail
In retail, a horizontal agent often sits in front of the customer. It helps answer general questions, guides visitors through the site, and handles simple support. These systems reduce wait times and keep people from dropping off.
A 2025 study on online shopping showed that returning customers who use chat during a session spend about 25% more than returning customers who do not use it. That is exactly the area where a horizontal agent adds value. It can answer a wide range of questions and keep people engaged.
Behind the scenes, a vertical agent supports stock planning, pricing and replenishment. It works with point of sale data, warehouse feeds and seasonal trends. Research from BCG shows that retailers using automated inventory planning cut stockouts by about 30% and improved inventory turnover by 25%.
Those gains come from systems that are tuned to retail logic, not from general chat. That is the role of a vertical agent. It focuses on one domain and makes sure the numbers are right.
In practice, you end up with both types working together. A general helper improves customer experience at the front of the store. A specialist engine protects margin and availability at the back.
Healthcare
Healthcare is a good example of why vertical agents matter. A horizontal agent can help staff with basic tasks like drafting discharge notes, explaining instructions in simple language, or answering common non-urgent questions. It supports the human team but does not make final decisions.
A vertical agent, on the other hand, is built around clinical or operational rules. It can help with triage flows, appointment routing, or claims coding. Studies on hospital operations show that tools that support documentation and virtual check-ins have freed up 10 to 15 percent of nursing time for direct patient care.
Another review of digital assistants in healthcare notes they can support triage, medication reminders, and patient education at scale. This kind of work needs fixed steps and clear safety checks, which suits a vertical agent.
So in healthcare, you will often see horizontal AI agent support staff communication and education. A vertical agent will work under strict guardrails in high-stakes flows like triage, billing, or scheduling.
Finance
Finance teams care about control, accuracy and speed. Here a horizontal agent can assist analysts, controllers and front office staff with research, report drafts, policy summaries or internal Q & A sessions. It saves time on information gathering and basic writing, but people still review and approve the final outputs.
Vertical agents in finance focus on concrete workflows. Examples include transaction monitoring, reconciliation, exception handling, credit checks or claims handling.
A 2024 industry survey reported that 58% of financial institutions link revenue growth to the use of automation and intelligent systems, mainly through better risk management and faster operations.
Another survey from NVIDIA showed that about 91% of firms in financial services now use some form of automated decision support or are piloting it. Those figures are driven mostly by vertical use cases where logic is clear, data is rich and output must be precise.
For you as a finance leader, the pattern is simple. Use horizontal agents to support thinking. Use vertical agents to support transactions.
Education
In education, a horizontal agent often acts as a general helper for teachers and students. Teachers use it to draft lesson ideas, create worksheets, plan activities or summarise resources.
A recent report found that about 60% of teachers have already added such tools into their daily routine, mainly for planning, content gathering and feedback. The same tools help students with research, explanations and practice questions.
Vertical agents in education focus on fixed flows such as placement tests, progress tracking or structured tutoring paths. They work with assessment rules, curriculum maps and skill frameworks rather than open questions.
One report noted that the global market for education systems that use automation is set to more than double between 2022 and 2025. Growth like that is driven by use cases where the system follows a defined structure, such as adapting question difficulty or generating progress reports for each learner.
If you look at a modern classroom or online program, you see both at work. A horizontal agent supports open learning and content creation. A vertical agent quietly shapes the learning path, scoring, and reporting.
Why Most Companies Will Use Both Together
You do not need to choose one or the other. The future belongs to blended systems, where one general agent routes tasks to a set of specialized agents.
This model improves speed, accuracy, and cost control. It mirrors how your teams work now. You have general staff, and you have specialists. This structure creates clarity and reduces risk.
According to McKinsey, companies that combine general and specialized automation see the strongest results, with productivity gains reaching 20 to 30 percent across core operations.
This combined approach lets you scale automation while staying in control of outcomes.
How We Build Vertical and Horizontal Agent Systems at Sthenos
At Sthenos, we design AI systems that match your goals and workflows. Our team builds horizontal agents that support many teams at once, and we build vertical agents that take on complex tasks in finance, operations, support, logistics, and compliance.
We work closely with your leaders to understand your data, your rules, and your processes. Then we design an agent system that improves speed, accuracy, and cost control without disrupting your teams. Our goal is to help you build automation that improves outcomes and reduces the load on your workforce.
Final Thoughts
Your choice between a vertical agent and a horizontal agent depends on what your teams need. If you want flexibility and fast adoption, a horizontal agent is right for you. If you need accuracy and repeatable results, a vertical agent will serve you better. If you want a true transformation, you will use both. This is how you get speed and precision at the same time.
When you partner with us, we help you build a system that supports your goals and moves your business forward. Schedule a consultation with one of our AI experts.